Leave Your Message
In the world of electronics, the term "Touch Button Spring" is becoming increasingly significant. Experts like Dr. Emily Larson, a leading engineer in the field, assert, "Touch Button Springs are crucial for user interface design." These components bridge functionality and user experience, making devices more intuitive and responsive.
Understanding how a Touch Button Spring operates is essential for any designer or engineer. This simple yet effective mechanism allows buttons to respond to a touch, creating seamless interactions. The springs provide both tactile feedback and durability, ensuring longevity in use. However, the design process can be complex. Ensuring the right balance between spring tension and responsiveness requires careful consideration.
Mistakes can lead to frustrating user experiences. If a Touch Button Spring is too stiff, users may find it hard to engage the button. On the other hand, if it’s too soft, it may not provide adequate feedback. Balancing these aspects is essential, yet it poses a challenge. As technology evolves, so does the demand for more advanced Touch Button Springs. This evolution invites reflection on what we can improve in design and functionality.

A touch button spring is a crucial component in various electronic devices. It allows a tactile response to the user when pressed. This simple mechanism is often overlooked but is essential for functionality. These springs work by compressing and expanding, providing feedback. When you press a touch button, the spring creates a satisfying click. This helps the user know their command has been registered.
The design of touch button springs varies. Some are made of metal, while others may use plastic. The material affects durability and responsiveness. A poorly designed spring can lead to inconsistent performance. It might feel too soft or too stiff. This inconsistency can frustrate users.
Visualizing a touch button in action clarifies its purpose. Imagine pressing a button on a remote. You feel a slight resistance followed by a click. This moment is facilitated by the spring inside. Its function is simple. Yet, when it fails, the entire device can feel unresponsive. The balance of design and user experience is important. Each spring must be engineered carefully to meet expectations.
A touch button spring is a fascinating mechanism. It consists of several key components that work together to create a reliable touch response. The main parts include the spring itself, a housing, and a contact plate. Each of these elements plays a vital role in the functioning of the touch button.
The spring is made of flexible metal, designed to compress and expand with pressure. When you press the button, the spring compresses. This motion activates the contact plate, which completes an electrical circuit. The interaction between these components is delicate. If any part is misaligned, the button may not work properly. This presents challenges during manufacturing and assembly.
The housing encapsulates these components, providing protection. It must be sturdy yet lightweight, enabling effective operation. In design, aesthetics are important too. Balance between form and function is key. A well-designed touch button spring improves user experience. However, design flaws can lead to malfunction. Continual testing helps refine this technology. Getting it right often requires numerous iterations and adjustments.
Touch button springs play a crucial role in the mechanics of touch-sensitive devices. These springs are designed to provide a tactile response when the user presses a button. Inside, they convert the mechanical motion into an electrical signal, enabling the device to register the action. The materials used, often a combination of metal alloys and plastics, influence the spring's durability and feel.
According to industry reports, the market for touch-sensitive technology is projected to grow by over 12% annually. This demand pushes manufacturers to innovate. They focus on optimizing spring design for better responsiveness. However, not all designs achieve the desired balance between sensitivity and longevity. Some springs may become unresponsive after frequent use, highlighting the need for ongoing evaluation.
Tips: Test multiple touch button springs to find the best fit for your project. Consider the environment in which they will be used. Choose springs that can withstand wear and tear in high-traffic situations. Regular maintenance checks can also ensure they remain operational. User feedback is vital for continuous improvement, as it can reveal hidden flaws in the design.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Touch Button Spring | A spring used in touch button devices to enable tactile feedback. | Creates a resistance that allows the user to feel a physical response when the button is activated. |
| Material | Typically made of stainless steel or other flexible materials. | Provides durability and the necessary tension for operation. |
| Tension | The amount of force required to compress or extend the spring. | Determines the sensitivity and response time of the button action. |
| Dimensions | Varies based on design requirements. | Affects the fit and functionality within the device housing. |
| Installation | Integrated into the button assembly of various electronic devices. | Ensures proper movement and return to original position after activation. |
Touch button springs find wide applications in various devices. They are essential in creating a responsive touch experience. Common uses include smartphones, remote controls, and home appliances. These springs facilitate a subtle yet noticeable tactile feedback when pressed. This feature enhances user interaction by confirming that the input was registered.
Tips: When choosing touch button springs, consider the actuation force. A spring that’s too stiff may frustrate users. Alternatively, a spring that’s too light might not register well. Balance is key.
In addition, the materials used for these springs play a significant role. The wrong material can lead to a poor response or even malfunction. Metal springs offer durability, while plastic options might reduce weight. Each choice has a trade-off.
Designing devices with touch button springs can be challenging. Achieving the right feel is a process that requires multiple iterations. Testing with real users can provide valuable insights. Their feedback helps refine the design for better performance.
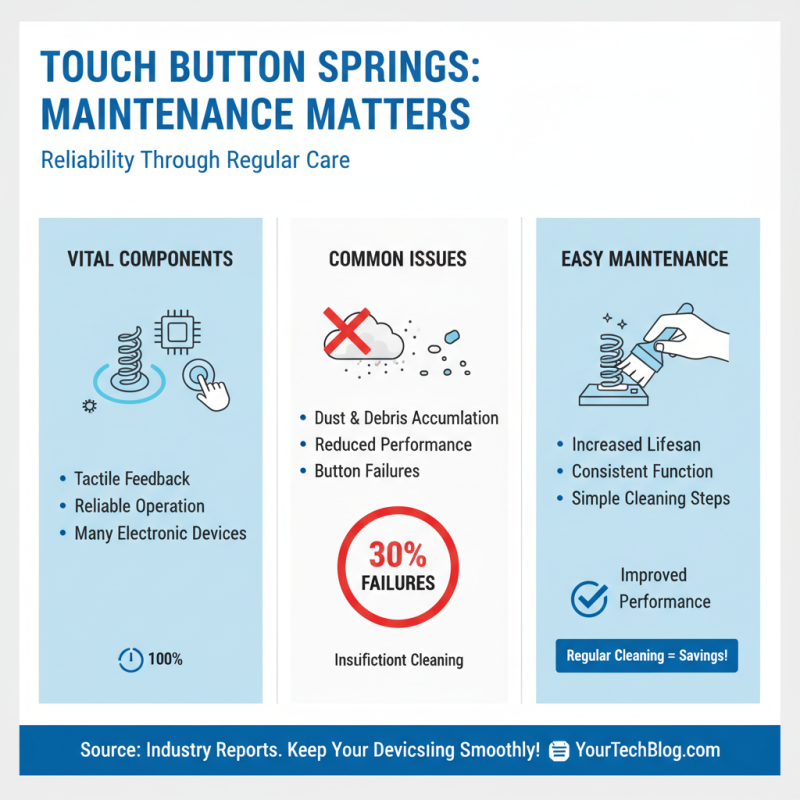
Touch button springs are vital components in many electronic devices. They provide tactile feedback and ensure reliable operation. Regular maintenance can significantly enhance their performance. Dust and debris are common issues that can affect functioning. According to recent industry reports, nearly 30% of failures in touch button components are linked to insufficient cleaning practices.
Troubleshooting touch button springs often starts with inspection. Look for signs of wear or misalignment. A study shows that proper alignment can improve efficiency by up to 20%. Lubrication plays a key role as well. Using appropriate grease can reduce friction and prolong lifespan. However, over-lubricating can lead to sticky buttons, which frustrates users.
Another common issue is inconsistent sensitivity. This can result from dirt accumulation in the spring mechanism. Regular cleaning with compressed air can help. It's also essential to check for corrosion, which can drastically impact performance. Regular maintenance checks are crucial, yet frequently overlooked. Studies indicate that devices with consistent upkeep enjoy a 15% increase in reliability compared to those without.