Leave Your Message
In the fast-evolving world of electronics, efficient handling and packaging of components is crucial for ensuring optimal production processes. One of the key solutions that has emerged to streamline this task is the SMD Electronic Component Carrier Tape. This specialized tape is designed to secure and transport Surface Mount Device (SMD) components, allowing for better organization and protection during assembly and manufacturing. Understanding the functionality and benefits of SMD Electronic Component Carrier Tape can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce the risk of damage to delicate components.
By utilizing SMD Electronic Component Carrier Tape, manufacturers can enhance their production workflows, ensuring that components are easily accessible and well-protected from external factors. This article delves into the specifics of how SMD Electronic Component Carrier Tape is structured, its applications in various electronic assembly processes, and provides effective strategies for use. With an emphasis on maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste, mastering the application of this essential tool could be a game-changer in the electronics industry.
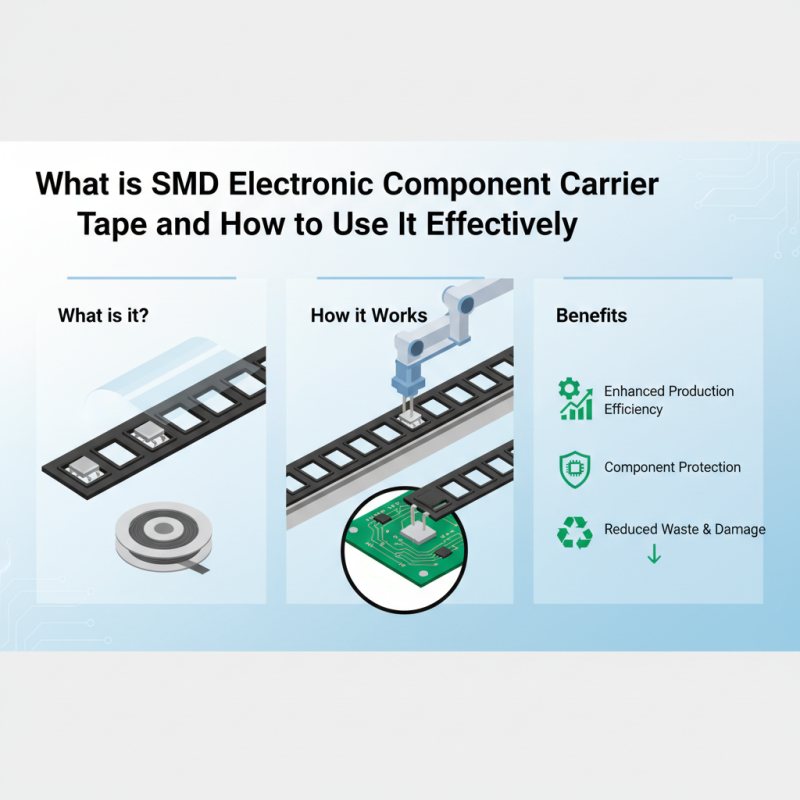
SMD electronic component carrier tape is an essential packaging solution designed for surface-mount devices (SMDs). This tape provides a secure and organized method for transporting and storing electronic components. Typically made from plastic or polyester, it features a series of pockets or cavities that perfectly fit the components, ensuring they remain in place and are protected from damage during handling and shipment. The standardized width and layout of the tape help streamline automated assembly processes, facilitating efficient pick-and-place operations in manufacturing environments.
To use SMD electronic component carrier tape effectively, it is crucial to select the appropriate type of tape based on the dimensions and specifications of the components being stored. Proper alignment of the tape with feeding systems in pick-and-place machines is also vital, as any misalignment can lead to improper placement of components on printed circuit boards (PCBs). Additionally, care should be taken to avoid exposing the carrier tape to excessive temperature or humidity, which could compromise the integrity of the tape and the components it houses. By following these best practices, manufacturers can enhance their production efficiency and minimize the risk of errors in the assembly process.
SMD carrier tapes are essential for the efficient handling and placement of surface-mounted devices (SMDs) in electronic manufacturing. There are primarily two types of SMD carrier tapes: embossed and perforated tapes.
Embossed carrier tapes are used for components with specific geometries, allowing for secure stacking and preventing movement during transportation. This type is ideal for smaller components like chip resistors and capacitors, where precision placement is crucial.
On the other hand, perforated carrier tapes are employed for larger components that require greater stability, such as connectors and IC packages.
Each type of tape has a distinct application based on the size and shape of the components being handled. For instance, embossed tapes are designed with pockets that tightly hold components, ensuring they remain in place, especially during high-speed assembly processes.
Perforated tapes, meanwhile, provide the flexibility needed for larger or irregularly shaped components, allowing for smooth feeding into placement machines. Understanding the differences between these carrier tapes and selecting the appropriate type based on component specifications helps enhance production efficiency and minimizes the risk of damage to sensitive electronic parts.
SMD (Surface Mount Device) carrier tape is an essential component in the handling and transportation of electronic parts. Understanding its key features can significantly enhance performance in manufacturing and assembly processes. One of the primary features of SMD carrier tape is its standardized dimensions, which allow for compatibility with various automated equipment. This uniformity ensures that the components are securely placed for precise and efficient assembly, reducing the likelihood of jammed machines or misplaced components.
Another critical attribute is the material used for the carrier tape. Typically made from high-quality plastic, the tape must provide adequate protection against both static electricity and physical damage. A well-engineered carrier tape minimizes the risk of component damage during transit. Moreover, the tape’s adhesive properties play a pivotal role in securely holding components in place while also allowing for effortless removal during assembly.
Tips: When selecting SMD carrier tape, ensure it meets industry standards for thickness and width to maintain compatibility with your equipment. Additionally, consider the reel size as it can affect the rate of production; using appropriately sized reels can optimize assembly line efficiency. Lastly, always store carrier tapes in a controlled environment to avoid degradation that could compromise the integrity of the electronic components.
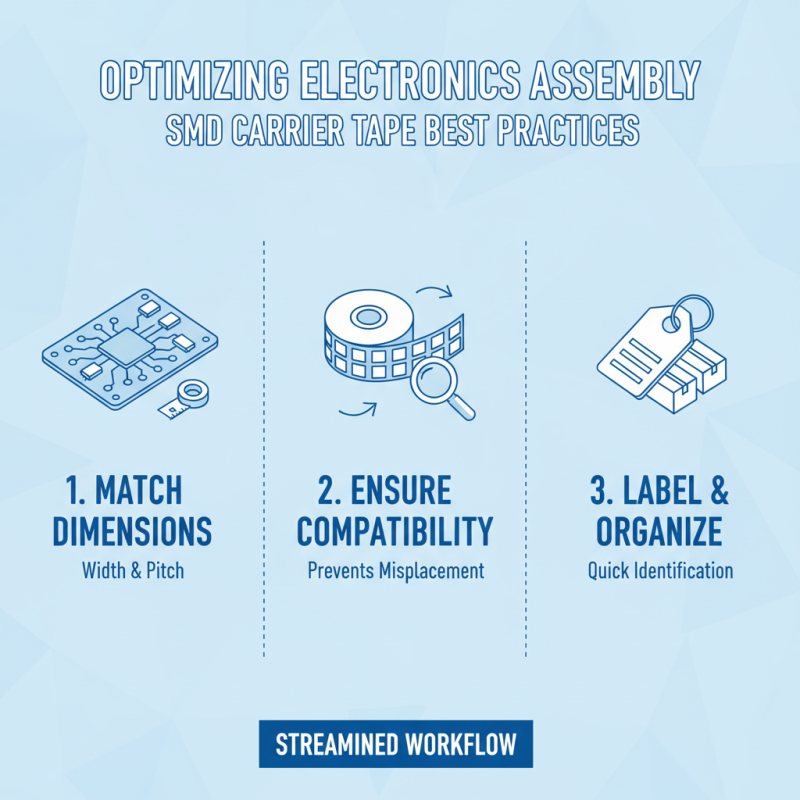
Effective use of SMD carrier tape is crucial for optimizing the workflow in electronics assembly. One of the best practices is to choose the appropriate tape width and pitch that match the components being utilized. When sourcing carrier tape, ensure that the dimensions align with the specifications of the SMD parts, as this will minimize the risk of misplacement or damage during transport and assembly. Proper labeling and organization of the tape can further enhance efficiency, allowing for quick identification and retrieval of components.
Another key practice is to maintain a clean and controlled environment while using carrier tapes. Dust, moisture, and static electricity can adversely affect component performance and reliability. Implementing anti-static measures, such as grounding work surfaces and using ionizing blowers, can significantly reduce the risk of electrostatic discharge that may damage sensitive SMDs. Additionally, regularly checking and calibrating dispensing equipment will ensure that components are delivered accurately and efficiently, contributing to a smoother assembly process.
When using SMD (Surface Mount Device) carrier tape in electronics manufacturing, troubleshooting common issues is crucial for ensuring efficiency and quality. One prevalent problem is improper alignment of components within the tape. According to the IPC-9850 standard, 50% of defects in SMD assembly are attributed to poor component placement, often arising from misaligned tape. To mitigate this, operators should routinely calibrate their equipment and ensure that the carrier tape is fed correctly into the pick-and-place machine, maintaining consistent tension throughout the process.
Another frequent issue is the damage to the components themselves during handling. A report from the Electronic Industries Alliance indicates that mishandling during the transition from the carrier tape to the assembly line can lead to up to a 20% increase in defective parts. Implementing soft-touch mechanisms and using correct tooling can significantly reduce the risk of damage. Regular training focused on proper handling techniques can also help minimize the likelihood of such issues, enhancing overall yield rates and operational efficiency in the manufacturing process. By addressing these common concerns effectively, manufacturers can optimize their SMD assembly operations and reduce waste.