Leave Your Message
In the ever-evolving landscape of electronics, selecting the right circuit board components plays a pivotal role in the success of any project. Expert engineer Dr. Emily Carter, a prominent figure in the field of electronics design, states, "Choosing the right components is not just about functionality; it's about the overall performance and reliability of your circuit." This perspective emphasizes the critical nature of component selection in ensuring that a project meets its intended objectives effectively.
From resistors and capacitors to specialized chips and connectors, the myriad of circuit board components available can be overwhelming. Each component has its own specifications, benefits, and trade-offs, making informed decision-making crucial. Understanding the specific needs of your project, such as power requirements, size constraints, and environmental factors, is essential to navigating the complexities of component choices successfully. By delving into the principles of circuit board components, designers can enhance product performance while minimizing potential setbacks during development and production.

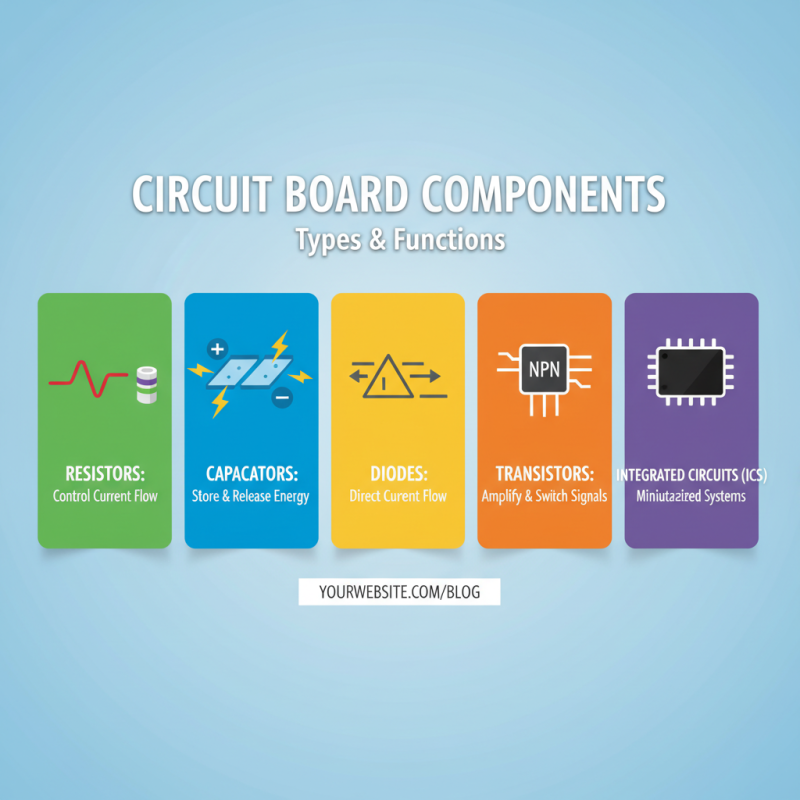
When embarking on a circuit board project, understanding the types and functions of various components is crucial. Circuit boards typically consist of resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits, each serving a unique purpose. Resistors control the flow of electric current, allowing for the adjustment of voltage levels within a circuit. Capacitors store and release electrical energy, making them critical for smoothing out signals and maintaining power stability. Diodes, on the other hand, ensure that current flows in one direction only, protecting sensitive components from potential damage.
Tips: When selecting resistors, pay attention to their power rating and tolerance to ensure they can handle the intended electrical load. For capacitors, consider factors such as capacitance value and voltage rating, which will determine their efficacy in smoothing out signal fluctuations.
Transistors act as switches or amplifiers, playing a significant role in signal processing and power management. Integrated circuits combine multiple components into a single package, simplifying design and reducing space on the circuit board. It's essential to choose the right type depending on your project specifications; for example, bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) are ideal for amplification, while metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) are excellent for switch operations.
Tips: When working with integrated circuits, always consult the datasheet for pin configurations and electrical specifications to avoid malfunction. Additionally, consider the thermal management of components to ensure optimal performance and longevity.

When selecting circuit board components for your project, understanding the specifications related to voltage, current, and power ratings is crucial. Voltage ratings indicate the maximum amount of voltage a component can handle without risk of failure. Exceeding this limit can lead to breakdown and potential damage. According to a recent study from the International Electrotechnical Commission, 70% of component failures are attributed to over-voltage conditions. Therefore, ensuring all components are rated adequately for your project’s voltage requirements is essential.
Current ratings, on the other hand, determine how much electrical current a component can safely carry. Components with inadequate current ratings may overheat, leading to circuit failure. It's advisable to choose components with a current rating that exceeds the expected load by at least 20%. This buffer can significantly enhance the reliability of your circuit. The IEEE standards recommend that engineers confirm their current ratings with real-world measurements, as datasheet values can sometimes be misleading.
### Tips:
1. Always check the temperature coefficients of components, as overheating can drastically reduce their performance.
2. Use simulation software to model the electrical characteristics before finalizing your design; this can prevent costly mistakes stemming from incorrect component selections.
3. Keep in mind the power ratings, which are calculated by the formula P=VI (Power = Voltage x Current). It's essential that the combined power ratings of your components align with the demand of your application to avoid inefficiencies or failures.
When selecting components for a circuit board, understanding the specific requirements of your application is crucial. Each type of application—be it radio frequency (RF), analog, or digital—has unique demands that influence component choice. RF applications often require components that can handle high frequencies and provide low-loss performance, necessitating careful selection of capacitors, inductors, and amplifiers. Components like low-noise figure amplifiers and high-frequency switches can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the RF circuit.
In contrast, analog applications prioritize linearity, bandwidth, and noise performance. Choosing operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors that align with the signal’s characteristics is essential to maintain signal integrity. Components with a high slew rate and low distortion are typically favored for applications in audio equipment or sensor circuits.
Lastly, digital applications focus on speed, power consumption, and logic levels. Here, selecting microcontrollers, logic gates, and memory components with appropriate specifications for data throughput and processing speed is essential. By aligning component choices with the specific technology and performance characteristics of RF, analog, or digital applications, designers can create efficient, reliable, and effective circuit boards tailored to meet project requirements.
When selecting circuit board components for your project, assessing quality and reliability is paramount. Adhering to industry standards can serve as a benchmark to ensure the components you choose meet necessary safety and performance requirements. Organizations such as IPC (Institute for Printed Circuits) provide guidelines that help in evaluating components' manufacturing processes, ensuring they undergo rigorous testing. These standards are designed to mitigate risks and enhance the longevity of your circuit boards.
To further verify the reliability of components, various testing methods should be employed. These include thermal cycling tests, vibration tests, and humidity tests, which simulate real-world conditions to assess how components would perform over time. For instance, thermal cycling can highlight potential failures due to thermal stresses, while vibration testing can identify weaknesses that may lead to mechanical failure.
Tips: Always prioritize sourcing components from suppliers that comply with these industry standards. It is advisable to request detailed test reports before making a purchase. Additionally, consider the component's lifecycle and performance data to ensure they can withstand the specific environmental conditions of your project. Regularly revisiting and evaluating these criteria will help maintain the integrity of your designs.
When embarking on an electronics project, one of the key challenges is achieving a balance between component quality and budget constraints. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis can help in identifying which components will yield the best performance without overshooting the project budget. According to industry reports, up to 70% of a project's total costs can be attributed to component selection, making this choice critical for project success. Choosing high-quality components can enhance the longevity and reliability of a product, yet opting for cheaper alternatives may lead to increased failure rates and replacement costs down the line.
Moreover, recent studies have indicated that approximately 30% of components used in electronic devices fail to meet quality standards, potentially resulting in costly recalls. Therefore, engineers must weigh the long-term benefits of reliability against immediate budget constraints. Utilizing platforms for benchmarking component prices and performance can facilitate informed decisions, helping teams select parts that not only fit their financial constraints but also ensure product success. Implementing a robust cost-benefit analysis framework can ultimately translate into improved project outcomes and enhanced customer satisfaction in the competitive electronics market.
| Component Type | Quality Rating | Cost ($) | Performance Score | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistor | High | 0.10 | 8.5 | Recommended |
| Capacitor | Medium | 0.25 | 7.0 | Consider |
| Microcontroller | High | 5.00 | 9.0 | Highly Recommended |
| Transistor | Low | 0.50 | 6.0 | Not Recommended |
| Inductor | Medium | 1.20 | 7.5 | Consider |