Leave Your Message
In the world of electronics, understanding circuit components is fundamental for anyone involved in design and innovation. As renowned electrical engineer Dr. Emily Johnson has stated, "The intricate dance of circuit components forms the backbone of modern technology, enabling devices to function seamlessly." From resistors and capacitors to transistors and diodes, each component plays a crucial role in the operation and efficiency of electronic circuits.
These components work together to control the flow of electrical current, store energy, and provide necessary feedback in a system. By analyzing their distinct functions, we gain insight into how electronic devices—from simple home appliances to complex computing systems—operate. This knowledge not only enhances our appreciation for technology but also empowers engineers and hobbyists to create more sophisticated and reliable electronic solutions.
As we delve deeper into the various types of circuit components and their specific roles, it becomes evident that mastering these elements is essential for anyone looking to innovate within the realm of electronics. Understanding these components and their interplay is not just a technical necessity; it is a pathway to unlocking the potential for future advancements in technology.
Passive circuit components are essential building blocks in electronic circuits, playing crucial roles in the transmission and management of electrical signals. Among the primary types of passive components are resistors, capacitors, and inductors, each serving specific functions that contribute to circuit performance. According to a recent report by the International Electrotechnical Commission, passive components are projected to constitute a significant portion of the global electronic components market, estimated to reach over $500 billion by 2025.
Resistors are fundamental in controlling current and voltage in circuits. They limit the flow of electric current, divide voltages, and can also be used for biasing active components. Capacitors, on the other hand, store and release electrical energy, acting as filters in power supply systems or coupling and decoupling AC signals in various applications. The growth of capacitors in the market is driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient devices, with a market forecast anticipating a growth rate of over 5% annually through the next few years.
Inductors store energy in a magnetic field and are crucial in filtering and energy management within circuits. They help in smoothing out fluctuations in power supply and are essential in applications such as switching power converters. Industry reports indicate that the use of inductors is aligned with the expanding automotive and industrial sectors, which increasingly require robust power management solutions.
Overall, understanding these passive components and their functions is vital for designing efficient electronic systems in today’s technology-driven world.
Active circuit components are essential elements in electronic circuits that require an external power source to operate and perform their functions. The most common types of active components include transistors, operational amplifiers, and integrated circuits. Each of these components plays a unique role in circuit design, enabling the manipulation of electrical signals.
Transistors, for example, serve as a fundamental building block in electronic devices. They can function as switches or amplifiers, controlling the flow of current in a circuit. By varying the input voltage to the transistor, it can regulate a larger output current, making it invaluable for signal processing and power management. Operational amplifiers, on the other hand, are used widely in analog circuits for various applications such as signal conditioning, filtering, and mathematical operations like addition and subtraction. Their high input impedance and low output impedance make them ideal for interfacing with different components.
Integrated circuits (ICs) encompass a variety of functions within a single package, often containing multiple transistors, diodes, and other components. These miniaturized circuits can perform complex tasks, such as data processing, signal amplification, and control functions in devices ranging from simple electronic gadgets to sophisticated computing systems. The versatility and efficiency of these active components significantly contribute to the advancements in modern electronics, facilitating the development of innovative technology solutions.
Specialized circuit components play a crucial role in modern electronic devices, with diodes and transistors being among the most significant. Diodes function primarily as rectifiers, allowing current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. This property is essential in power supply circuits, where they convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). According to a recent industry report, the global diode market is projected to reach approximately $15 billion by 2025, driven by the expanding adoption of renewable energy technologies.
Transistors, on the other hand, serve as vital building blocks for amplification and switching applications. They can control electrical signals, making them indispensable for everything from small battery-operated devices to large-scale computing systems. The semiconductor market, which includes transistors, is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% through 2027, reflecting the increasing demand for faster and more efficient electronic components in various industries.
Tip: When designing circuits, it is essential to carefully consider the specifications and operating conditions of your diodes and transistors to ensure optimal performance. Ensure that the maximum current and voltage ratings are not exceeded to prevent component failure.
Another important aspect to keep in mind is the thermal management of these components. Overheating can lead to reduced efficiency and even permanent damage. Incorporating adequate heat sinks and maintaining proper ventilation in your circuit designs can significantly enhance reliability and longevity.
Integrated circuits (ICs) are fundamental components in the realm of electronics, serving as the backbone for modern devices. They are constructed from semiconductor materials and can contain thousands to millions of tiny components, such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors, all etched onto a single chip. According to the International Data Corporation (IDC), the global market for semiconductor devices, including ICs, is projected to reach over $600 billion by 2025, reflecting the increasing demand for compact, powerful, and energy-efficient solutions in various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications.
The functionality of integrated circuits spans a wide array of applications, from simple logic operations to complex processing tasks. They enable the miniaturization of electronic circuits, significantly reducing the size and cost of devices while enhancing performance and reliability. A report from MarketsandMarkets indicates that the adoption of integrated circuits in automotive electronics is expected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 8% through 2024, driven by the growing trend towards electric vehicles and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). This demonstrates the critical role ICs play in driving innovation across multiple industries, facilitating advanced features and functionalities that define modern electronics.
| Component Type | Function | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | Limits current flow and divides voltages | Current limiting in LED circuits |
| Capacitor | Stores electrical energy and smooths out fluctuations | Filtering applications in power supplies |
| Inductor | Stores energy in a magnetic field, resists changes in current | Used in filtering and tuning circuits |
| Diode | Allows current to flow in one direction only | Rectifying AC to DC |
| Transistor | Amplifies or switches electronic signals | Used in amplifiers and logic gates |
| Integrated Circuit (IC) | Combines multiple circuit functions into a single package | Used in microcontrollers and amplifiers |
| LED (Light Emitting Diode) | Emits light when current flows through it | Lighting and display applications |
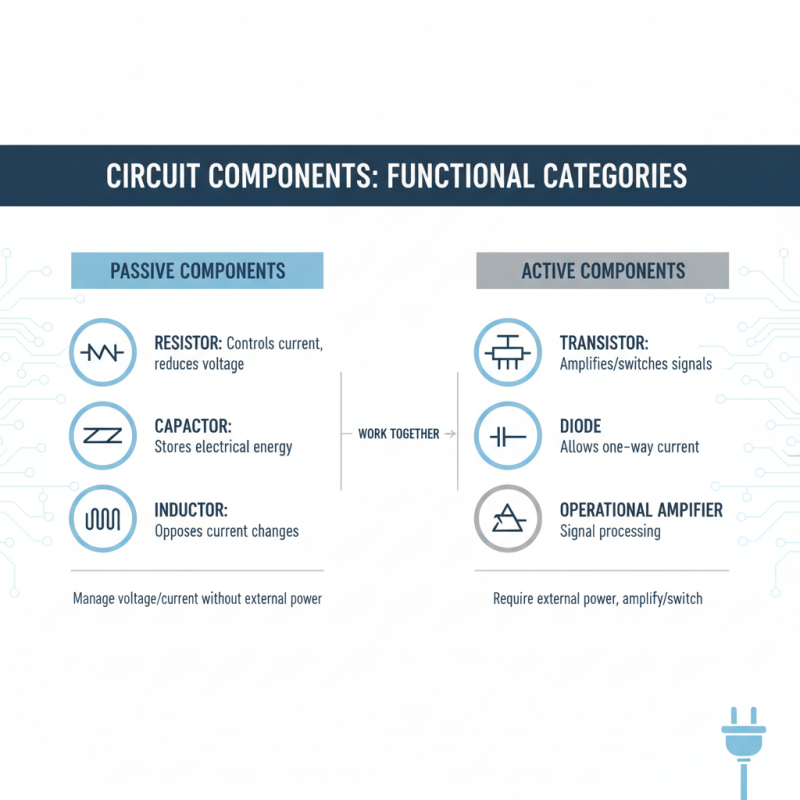
Circuit components can be categorized based on their functionality, which helps in understanding their distinct roles in electrical and electronic circuits. Passive components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, play foundational roles by managing voltage and current flow without requiring an external power source. Resistors control current and reduce voltage levels, capacitors store electrical energy temporarily, and inductors oppose changes in current, each contributing uniquely to signal processing and energy management in a circuit.
On the other hand, active components like transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits (ICs) rely on an external energy source to perform their functions. Transistors can amplify signals and switch currents, which is crucial for digital circuits and signal modulation. Diodes, allowing current to flow in one direction, serve essential roles in rectification and protection. Integrated circuits, which encapsulate multiple components into a single unit, enhance functionality and reduce size, making them central to modern electronics. By analyzing these components based on their functionality, it becomes clear how they collaborate to manipulate and process electrical signals, driving innovation in circuit design and application.