Leave Your Message
In the rapidly growing world of electronics, choosing the right PCB touch button can significantly impact your project's success. According to a recent industry report by Electronics Research Institute, the demand for innovative interface solutions, like PCB touch buttons, has surged by 25% in the last two years. With this surge comes the need for informed decisions and specific criteria to evaluate options.
Expert insights from Adam Keene, a leading figure in PCB design, emphasize that “understanding the nuances of touch sensitivity is crucial.” This highlights the importance of selecting a PCB touch button that not only fits the design but also enhances user experience. Factors such as tactile feedback, durability, and compatibility with various materials are paramount.
However, choosing the best option can be challenging. Many designers overlook crucial specifications. This oversight can lead to design flaws or user dissatisfaction. Therefore, taking a holistic approach to research and selection is essential. Only then can designers ensure their PCB touch buttons meet functional and aesthetic requirements.

PCB touch buttons are becoming increasingly popular in modern electronics. They offer a sleek design and eliminate the need for mechanical switches. Understanding their functionality is essential for choosing the right component for your project. These buttons work by detecting changes in capacitance when a user touches the surface.
According to a report from MarketsandMarkets, the touch sensor market is projected to reach $27.3 billion by 2024, growing at a CAGR of 10.4%. This growth illustrates the rising demand for touch-sensitive components across various industries, including consumer electronics and automotive applications. The ability to integrate touch technology seamlessly in devices enhances user experience and functionality.
Tips: Consider the environment where the PCB will be used. Factors like dust, moisture, and temperature can affect the performance of touch buttons. Testing under realistic conditions is critical. Also, pay attention to the sensitivity settings. Too much sensitivity may lead to false activations, while too little can frustrate users.
As you select a PCB touch button, consider the available interfaces and compatibility with your microcontroller. Some buttons require specific coding for proper integration. This process can be complex, and developers should prepare for potential troubleshooting. Overall, understanding the complexities of PCB touch buttons can lead to better designs and improved user interaction.
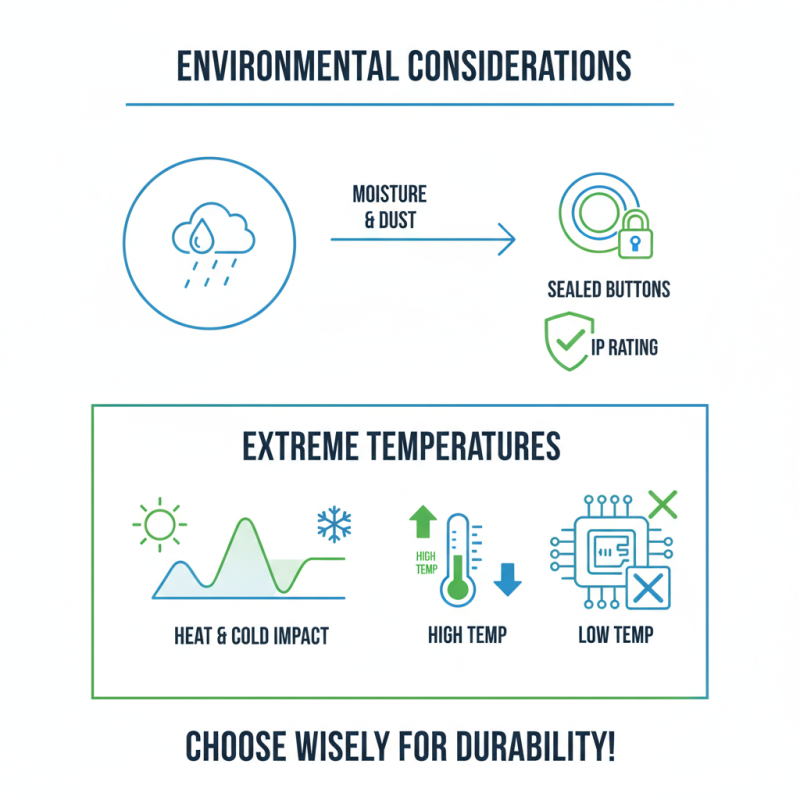
When selecting a PCB touch button, consider the environmental conditions. Does the button need to withstand moisture or dust? High-humidity areas require sealed buttons. Check the IP rating to ensure durability. Some buttons don’t perform well in extreme temperatures. Evaluate how heat or cold might affect your project.
Next, think about the touch sensitivity. Different applications have varying requirements for responsiveness. You want a button that registers a touch but won’t trigger from accidental brushes. Testing prototypes can save you from frustration later. Look at the tactile feedback as well. Users often prefer a slight click or resistance to feel more confident in their selection.
Aesthetics also matter. The size and shape of your button should complement your overall design. Skimping on this could detract from user experience. Does your design plan allow for a minimalist look? Or is a pronounced button needed? Evaluate how various colors look on the PCB. Ultimately, the selection process requires thoughtful consideration. It’s easy to overlook these aspects, leading to future headaches.
Selecting the right PCB touch button can be challenging. Various types, including capacitive, resistive, and mechanical buttons, each offer unique benefits and limitations. A recent industry report revealed that capacitive touch buttons are gaining popularity. They account for approximately 40% of the market share, making them a strong contender for many projects.
When choosing, consider the environment. Capacitive buttons perform well in clean settings. However, they may struggle in harsh conditions, where resistive buttons shine. Mechanical buttons, while less elegant, provide tactile feedback that's helpful in various applications. Their simplicity can be an advantage, particularly in projects where reliability is paramount.
**Tips:** Assess your project requirements carefully. Think about the expected lifespan and durability of the button. For many, tactile feedback is important. Striking a balance between usability and design is essential. Don't overlook the significance of user experience. Engaging users is key, and the type of button can significantly impact your project's success.
| Type of PCB Touch Button | Sensing Technology | Operating Voltage | Sensitivity | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacitive Touch Button | Capacitive Sensing | 3V - 5V | High Sensitivity | Smartphones, Tablets |
| Resistive Touch Button | Resistive Sensing | 3V - 12V | Medium Sensitivity | Industrial Equipment, Control Panels |
| Optical Touch Button | Optical Sensing | 5V - 12V | Very High Sensitivity | Interactive Displays, Kiosks |
| Mechanical Touch Button | Mechanical Switch | 5V - 15V | Low Sensitivity | Home Appliances, Automobiles |
| Ultrasonic Touch Button | Ultrasonic Sensing | 5V - 12V | Medium-High Sensitivity | Accessibility Devices, Robotics |
When evaluating the quality and durability of PCB touch buttons, a few key factors come into play. Start by examining the materials used in the buttons. High-quality polymers often withstand wear and tear better than cheaper options. Look for buttons that resist fading and discoloration over time. They should also handle various environmental conditions like humidity and temperature fluctuations without degrading.
Testing is an essential part of the selection process. Perform hands-on tests to see how the button responds to touches. Are they overly sensitive, or do they require significant pressure? Consider how often the button will be used as well. Frequent usage can lead to quicker wear, so durability is critical. Monitor how well the button maintains functionality after extensive use. This aspect is often overlooked but vital for long-term projects.
Another point to reflect on is the design of the touch button. Aesthetics matter, but they should not compromise functionality. Sometimes, a beautifully designed button may fail in practicality. Choose a balance between appearance and performance. Additionally, read feedback from other users. Remember that experiences can vary, and what worked for someone else may not work for you. ط
When integrating PCB touch buttons into your project, consider your design's ergonomics. Placement matters. Ensure buttons are easy to access and use. Think about user interaction. Design should encourage intuitive use. Users may struggle if buttons are out of reach.
Tips: Test the button's responsiveness. A good touch button should react quickly and accurately. Experiment with different sensitivity settings. Too sensitive can lead to accidental presses, while not sensitive enough can frustrate users.
Material choice for the PCB is critical. Consider environmental conditions it will face. Humidity, dust, and temperature can impact performance. Some materials may not withstand harsh conditions. Research potential challenges early in your design process.
Tips: Gather feedback during the testing phase. Observe users interacting with the buttons. Make adjustments based on their experiences. This feedback loop can reveal unforeseen issues and improve usability.